Physical Address
60 Ekwema Cres, Layout 460281, Imo
Physical Address
60 Ekwema Cres, Layout 460281, Imo
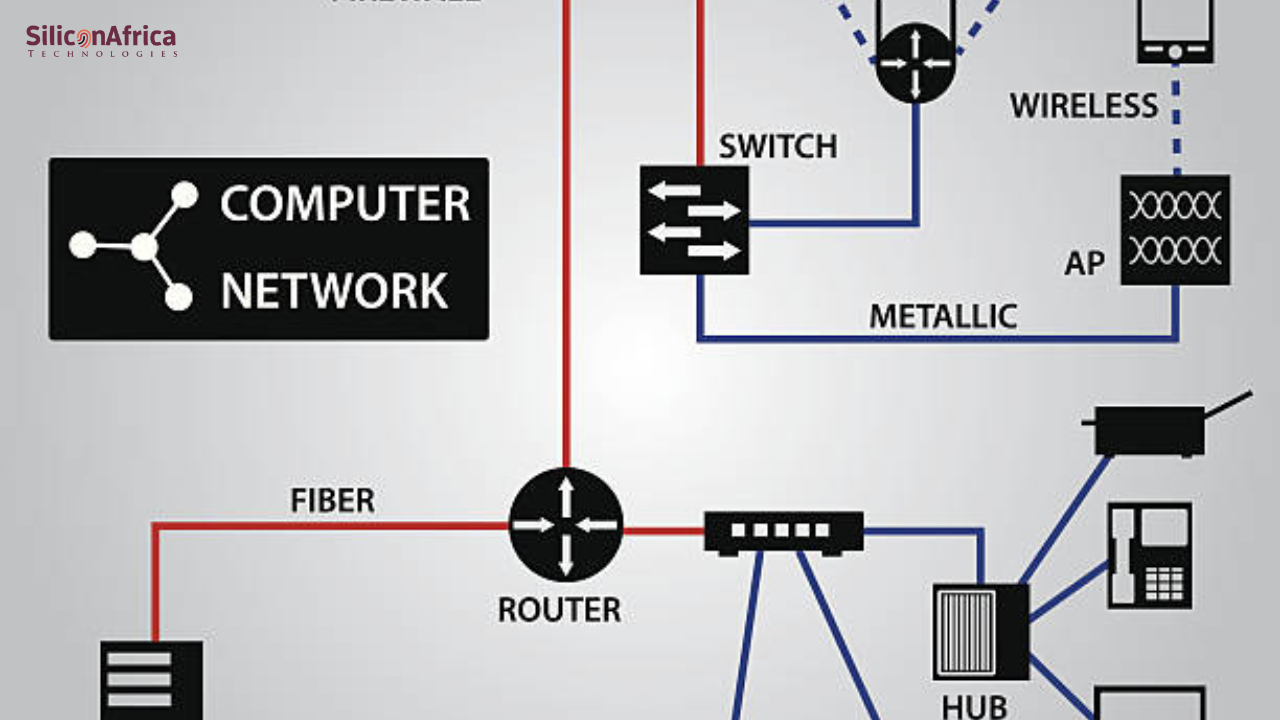
Network topology is how devices and connections are arranged within a network, either physically or logically in a computer. It outlines how gadgets connect and how data moves between them.
There are several broad categories of network topology. This guide will break down the various types of network topologies and their uses.
Read on to find out more.
Network topology is all about the physical and logical layout of devices and connections in a network. The physical topology explains how cables and devices are laid out, while the logical topology describes how data travels through the network, no matter the physical layout.
Both play big roles in a network’s performance, ability to scale, and security. Each type has its strengths and limitations, and the right choice depends on what the network needs to do.
See also: Starlink To Offer Satellite Internet Directly To Phones
Network topologies in fields like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) help organize how data flows and tasks are handled. Some popular topologies include:
Do you have issues with charging your phone? Check out 6 major things stopping your phone from charging fast.
See also: My Network is Slow: How to Boost Your Network in Nigeria
There are several types of network topologies you’ll see in computer networks:
In bus topology, a single cable (the bus) links all network devices, acting as the backbone. Each device taps into this main cable to share data, which flows in one direction.
When data reaches the end, a terminator clears it from the line. A bus topology works well for small setups where one computer acts as a server and others as clients.
In a ring topology, each computer connects to two others, creating a circle or “ring.” A central station monitors the data flow, and only computers holding a “token” can send data, passing the token along when done. This type is common in networks where devices need clear, organized data transfer.
Mesh topology provides multiple paths for data, linking devices with numerous redundant connections. While complex, mesh setups are reliable because data can take different paths if needed.
Full mesh topologies link every device, while partial mesh only connects some. The internet often uses mesh topology for its reliability.
See also: Latest Update on Airtel Night Plan Code & How to Subscribe
Often called a “hierarchical” or “star-bus” topology, a tree topology has a root node connected to various other nodes in a branching layout.
Data flows from top to bottom or vice versa, making it ideal for structured networks. But if the main backbone fails, the entire network is at risk.
A hub or central node connects all devices in a star topology. It’s popular in local area networks (LANs) because it’s cheap and easy to set up. Devices connect individually to the hub, making troubleshooting easy.
Hybrid topologies mix two or more basic setups. For example, a star-bus topology combines features of star and bus topologies. It’s adaptable and can work well for more complex networks.
See also: How to Know if Your Phone Has Been Tapped (Full Guide)
In simple terms, what’s network topology?
Network topology is the arrangement of devices and connections in a network, describing how everything links up physically or logically.
How many types of network topology are there?
There are six main types: bus, ring, mesh, tree, star, and hybrid.
Which network topology works best for small businesses?
Star topology is ideal for small businesses since it’s affordable, easy to set up, and expandable if more devices need to join.
Which network topology is the most reliable?
Mesh topology wins for reliability because data can travel through multiple paths, but it’s also one of the pricier options.
What’s the most common topology?
The star topology is widely used due to its simple setup and ease of adding or removing devices without major issues.
No single topology is perfect for every network. The right choice depends on factors like cost, scalability, and how much reliability is needed. Consider your network goals when picking a topology to get the best results.
If you find this article helpful, please share your thoughts in the comment section and follow us on our social media platforms: X (Silicon Africa (@SiliconAfriTech)), Instagram (SiliconAfricaTech), and Facebook (Silicon Africa).