Physical Address
60 Ekwema Cres, Layout 460281, Imo
Physical Address
60 Ekwema Cres, Layout 460281, Imo
Imagine you have a delicious new app you want everyone to know about. But how do you reach the right people? This is where ad networks come in.
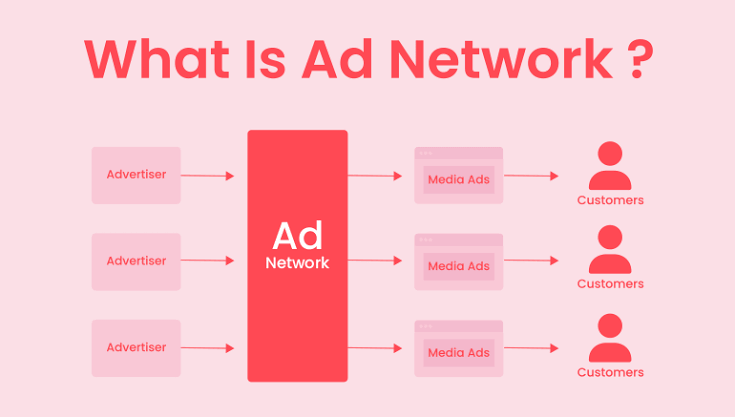
They’re like matchmakers for the digital world, connecting you (the advertiser) with websites and apps (the publishers) that can show your ad to potential customers.
So, what exactly is an ad network? In simple terms, it’s a platform that brings advertisers and publishers together. Publishers have spaces on their websites or apps where ads can be displayed.
Ad networks collect these unused spaces, called ad inventory, from many publishers and make them available to advertisers like you.
This gives you access to a vast audience without contacting each publisher individually.
Think of it like this: Imagine a bustling marketplace. Publishers have stalls with empty shelves (their ad inventory).
The ad network acts as the organizer, gathering all the stalls and filling them with different products (advertisements) from you and other businesses.
Read on to know more about ad networks!
As earlier stated, an ad network acts as a connector between advertisers and publishers. It collects unsold ad space from different publishers and offers it to advertisers who want to place their ads.
This collection allows advertisers to access many websites and apps, helping them reach specific audiences without needing to negotiate with each publisher individually.
Ad networks gather data about user behavior, demographics, and interests to match ads with the right audience.
This not only makes advertising campaigns more effective but also improves user experience by showing more relevant ads.
To understand how an ad network works, let’s look at its main parts:
1. Advertisers: Advertisers are businesses or individuals wanting to promote their products or services. Their main goal is to create successful ad campaigns that attract traffic, generate leads, or boost sales. They use ad networks to reach more potential customers without needing many connections with individual publishers.
2. Publishers: Publishers own digital platforms like websites or mobile apps where ads can be shown. They can range from large media companies to individual bloggers. Publishers provide ad inventory, spaces available for ads, and earn money by displaying ads from the ad network.
3. Ad Inventory: Ad inventory is the available space for ads on publisher websites or apps. This includes banner ads, video ads, and native ads. The amount and quality of this inventory are crucial for how well an ad network can serve its advertisers.
Read Next: What is Network Database Model? | SAT”
Ad networks can be grouped into different types based on how they work and who they target:
1. Contextual Ad Networks: These networks show ads based on the content of a webpage. For instance, an article about gardening might display ads for gardening tools or seeds.
2. Behavioral Ad Networks: Behavioral networks track users across different sites and show ads based on their browsing history and interests, aiming for better engagement.
3. Retargeting Ad Networks: These networks focus on bringing back users who have previously interacted with a brand but didn’t make a purchase, often using cookies to monitor behavior.
4. Display Ad Networks: Display networks mainly show visual ads like banners on various websites. They are among the most common types of ad networks today.
5. Mobile Ad Networks: These networks specialize in serving ads on mobile devices and cater specifically to mobile app developers and advertisers targeting mobile users.
6. Video Ad Networks: These networks focus on delivering video advertisements across platforms that support video content, such as streaming services or social media channels.
To understand how ad networks function, we need to look at several key processes:
Ad networks start by gathering available ad spaces from various publishers into one pool of inventory.
This gives advertisers access to a wider range of placements than if they negotiated directly with each publisher.
Once everything is set up:
Ad networks use different payment models:
Ad networks provide many benefits for both advertisers and publishers:
1. Access to Diverse Ad Inventory: Advertisers can reach audiences across various platforms without needing direct relationships with each publisher.
2. Targeted Ad Placement: Advanced targeting options help advertisers reach specific demographics, improving campaign effectiveness.
3. Monetization Opportunities for Publishers: Publishers can easily earn money from their content by connecting with multiple advertisers through one platform.
4. Simplified Ad Management: Both parties benefit from streamlined processes for managing campaigns and tracking performance metrics.
Read Next: What is Metropolitan Area Network? | Man Network
Even though there are many advantages, using ad networks also has challenges:
1. Transparency and Viewability Concerns: Advertisers often worry about whether real users see their ads or if they are placed in low-quality environments.
2. Ad Fraud and Brand Safety Issues: The risk of click fraud or inappropriate placements can damage trust in ad networks.
3. Balancing Interests: Finding a balance between advertiser demands for visibility and publisher needs for revenue can be tricky.
4. Adapting to Regulations: Changes in privacy laws require ongoing adjustments in targeting strategies for both advertisers and publishers.
In conclusion, knowing what an ad network is shows its vital role in today’s digital advertising strategies. By efficiently connecting advertisers with publishers, these platforms enable targeted advertising while maximizing revenue opportunities for content creators.
As technology continues to advance, so will the capabilities of ad networks, likely incorporating more sophisticated data analytics and machine learning techniques to improve targeting accuracy even further.
Future trends in this industry suggest continued growth in programmatic advertising, greater reliance on first-party data due to privacy regulations, and an ongoing push towards transparency in advertising practices, all essential for maintaining trust among users, advertisers, and publishers alike.
An ad network connects advertisers with publishers while an ad exchange is a real-time auction platform where advertisers bid on ad impressions.
Ad networks earn revenue by charging advertisers for placing ads and sharing part of that revenue with publishers.
Yes, small businesses can benefit from using ad networks as they provide access to a wide range of ad inventory and targeting options.
Some well-known ad networks include Google AdSense, Media.net, and AdMob.
clearcode.cc– What Is an Ad Network and How Does It Work?
www.criteo.com– What is an ad network? A guide for advertisers and publishers
www.paved.com– Ad Network FAQs for Advertisers
www.adjust.com– What is an ad network?Recommendations
What is a Mastermode? Definition and purpose in blockchain network
What Network is 08100 in Nigeria? | Network provider