Physical Address
60 Ekwema Cres, Layout 460281, Imo
Physical Address
60 Ekwema Cres, Layout 460281, Imo
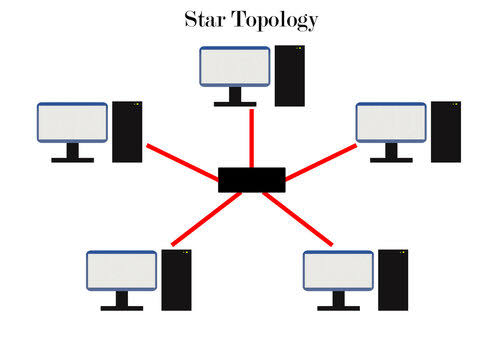
Imagine a network where all devices are connected to a single central point, like spokes on a wheel. This is the star network, a common topology in computer networking.
A star network is straightforward: each device, like a computer or printer, is directly linked to a central hub.
This hub acts as the traffic controller, managing all data flow between the connected devices. Why should you care about star networks?
Whether you’re setting up a home network or managing a large corporate network, understanding star networks is crucial.
It’s a foundational concept in networking, and it’s used in many different applications.
In this article, we’ll talk about star networks. We’ll explore their advantages and disadvantages, how they work, and where they’re most commonly used.
A star network is a way of organizing a computer network where a central device, like a switch or a router, acts as the hub that all the other devices connect to.
These other devices, such as computers, printers, or other gadgets, are the peripheral nodes that communicate directly with the central hub.
The characteristics of a star network include:
Read Next: What is SSID Network? How to Find & Protect Yours
Star network has its own share of advantages and disadvantages, and they include:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Understanding how a star network operates involves examining its communication flow and the devices involved. Here’s how it works:
Read Also: What is a Mastermode? Definition and purpose in blockchain network
Star networks are versatile and are applied across various domains, such as:
1. Small-scale Networks (e.g., Home, Small Office): Ideal for home networks where multiple devices connect to a single router for internet access.
2. Enterprise Networks (e.g., Corporate, Campus): Commonly used in business environments to link computers, printers, and other equipment through centralized switches or routers.
3. Wireless Networks (e.g., Wi-Fi, Bluetooth): Many wireless setups adopt star topology principles by connecting devices through an access point or router.
4. Industrial Automation and Control Systems: Used in manufacturing environments where machines need reliable communication through centralized control systems.
When evaluating networking options, it’s important to compare star networks with other topologies.
Here is a tabular comparison of star network to other network topologies:
| Topology | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Star | All nodes connect to one central hub | Easy management; fault isolation | Single point of failure |
| Bus | All devices share a single communication line | Cost-effective; simple setup | Difficult fault detection; performance degrades with more devices |
| Ring | Each device connects to two others forming a circle | Predictable performance; easy troubleshooting | Failure in one device affects entire network |
| Mesh | Every device connects directly to every other device | Highly reliable; robust against failures | Complex installation; expensive |
Factors such as cost, scalability, reliability, and ease of maintenance should be considered when choosing an appropriate topology for specific needs.
Read Next: What Network is 08100 in Nigeria? | Network provider
Understanding what a star network is and how it operates is vital for effective network design.
Its centralized structure offers numerous advantages such as ease of management and enhanced security while also presenting challenges like dependency on the central node.
As technology evolves, so too will networking strategies; therefore, staying up-to-date on network topologies will be vital for future developments in this field.
Yes, star topology offers good security because all data flows through a central switch or hub, making it easier to monitor network traffic and isolate issues quickly.
Yes, star topology can be implemented wirelessly using access points that serve as the central node connecting various wireless devices.
If the central hub fails, all connected devices will lose communication capabilities since they depend on this single point for data transmission.
Yes, hybrid topologies can be created by combining star topology with others like bus or ring configurations to meet specific networking needs.
www.javatpoint.com– What is Star Topology?
www.geeksforgeeks.org– What is Star Topology?
en.wikipedia.org– Star network
www.techtarget.com– Definition star network
What is Metropolitan Area Network? | Man Network
What is Roaming in Network? How Does it Work?