Physical Address
60 Ekwema Cres, Layout 460281, Imo
Physical Address
60 Ekwema Cres, Layout 460281, Imo
What is a ring network? This question might seem simple, but it delves into a fundamental concept in computer networking.
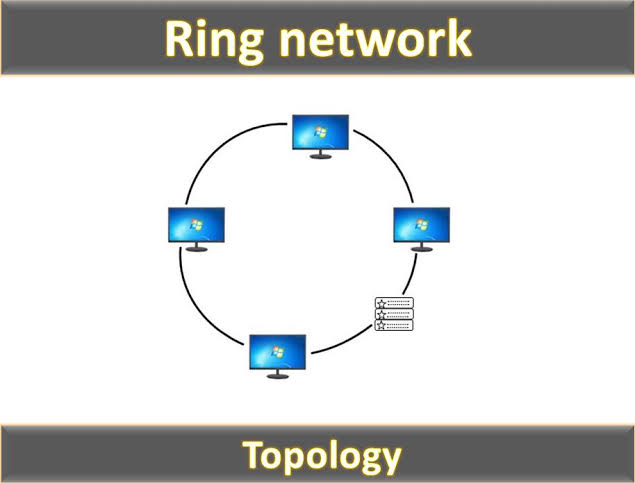
A ring network is a type of topology where devices are connected in a circular fashion, forming a closed loop.
Data travels in a single direction around the ring, making its way from node to node until it reaches its destination.
This seemingly straightforward configuration offers a unique blend of advantages and disadvantages, making it a valuable tool in certain networking scenarios.
This article will explore the definition, workings, advantages, disadvantages, applications, and significance of ring networks in modern networking.
A ring network is a network topology characterized by a circular arrangement of devices, where each device is connected to exactly two others, forming a continuous loop.
Data is transmitted unidirectionally around the ring, passing through each node until it reaches its destination. To ensure orderly data transmission, a token-passing mechanism is often employed.
A special token circulates around the ring, and only the node possessing the token has the permission to transmit data. This prevents collisions and ensures efficient utilization of the network.
Ring networks are known for their fault tolerance, as a single point of failure (e.g., a cable break or node failure) does not necessarily disrupt the entire network.
Data can still be transmitted around the ring, bypassing the faulty component. However, they can be more complex to configure and maintain compared to other topologies.
While less common today compared to other network topologies, ring networks continue to be used in specific scenarios where high reliability and fault tolerance are critical, such as in industrial automation, telecommunications, and redundant backup systems.
On that note, what are the characteristics of ring network topology?
A ring network is defined by its circular arrangement of nodes. Each device in this topology connects to two others, creating a closed loop.
This structure allows data to be transmitted in one direction (unidirectional) or both directions (bidirectional), depending on the design.
1. Circular Arrangement of Nodes: In a ring network, every node connects to two adjacent nodes, forming a continuous loop. This setup ensures that data can flow seamlessly from one device to another until it reaches its destination.
2. Data Transmitted in One Direction: Most ring networks operate in a unidirectional manner, meaning that data packets travel around the ring in a single direction. This reduces the chances of data collision and enhances overall network efficiency.
Therefore, the components of a ring network include:
Read Next: What is a Mastermode? Definition and purpose in blockchain network
Data transmission in a ring network is a well-orchestrated process. Each node receives data, processes it, and then retransmits it to the next node in the ring. This continues until the data reaches its final destination.
Here’s how it works:
The process of transmitting data in a ring network involves several steps:
A pivotal concept in ring networks is token passing, which governs how nodes access the network:
Ring networks offer several advantages that make them suitable for specific networking scenarios:
While ring networks offer several advantages, they also have some limitations:
Read Next: What is the Value of Pi Network | SAT
Ring networks find utility across various domains, such as:
While ring networks may not be as prevalent as other topologies like star or bus networks, they still hold significant importance in modern networking:
When compared with other topologies like star or bus configurations:
| Features | Ring Network | Star Network | Bus Network |
| Data Transmission | Unidirectional | Centralized | Linear |
| Collision Management | Low (Token Passing) | Moderate | High |
| Scalability | Moderate | High | Low |
| Fault Tolerance | Moderate (with dual rings) | High | Low |
Despite being considered somewhat outdated compared to more modern topologies like star or mesh networks, understanding ring networks remains relevant.
They provide foundational knowledge essential for grasping current networking technologies and practices.
Additionally, their principles continue to influence new designs aimed at optimizing performance and reliability in various applications.
Read Next: What is Network Database Model? | SAT
In summary, understanding what a ring network is, its structure, functionality, advantages, disadvantages, applications, and significance, provides valuable insights into networking principles.
As technology continues to advance, recognizing these foundational concepts will help professionals adapt and innovate within an ever-changing digital landscape.
Looking ahead, trends such as increased integration with IoT devices and advancements in redundancy measures may breathe new life into ring networks while continuing their legacy as an essential part of networking history.
Yes, ring networks can be combined with other topologies to create hybrid networks. For example, a ring network can be combined with a star topology to improve fault tolerance and scalability.
In a ring network, data collisions are typically avoided through the use of a token-passing mechanism. Only the node that possesses the token can transmit data. This prevents multiple nodes from transmitting simultaneously, thereby eliminating the possibility of collisions.
A node failure in a ring network can disrupt the flow of data. However, if the network is designed with redundancy, such as redundant links or alternate paths, the impact of a node failure can be minimized. In some cases, the network may automatically reconfigure itself to bypass the failed node.
Ring networks generally offer better performance and reliability than bus networks. In a bus network, a single point of failure can disrupt the entire network. In contrast, ring networks can tolerate single-point failures due to their circular topology. Additionally, ring networks can provide higher bandwidth and lower latency compared to bus networks.
unstop.com– Ring Topology – Basics| Applications | Advantages | Disadvantages
www.zenarmor.com– Ring Topology: Definition, Practices, and Importance
www.geeksforgeeks.org– Advantages and Disadvantages of ring topology
What is SSID Network? How to Find & Protect Yours
What is Metropolitan Area Network? | Man Network