Physical Address
60 Ekwema Cres, Layout 460281, Imo
Physical Address
60 Ekwema Cres, Layout 460281, Imo
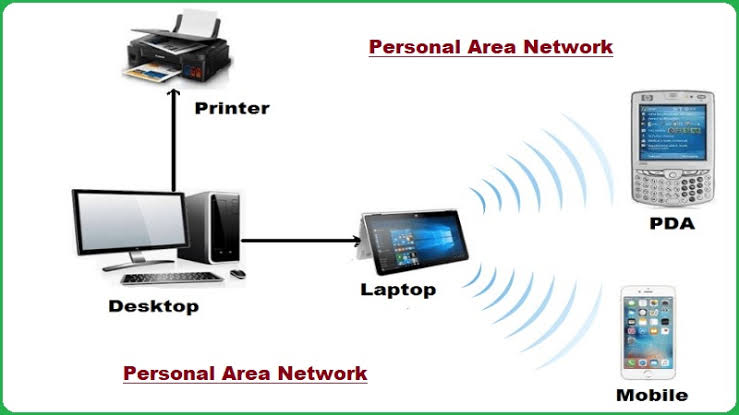
Have you ever wondered how your smartphone seamlessly connects to your wireless headphones or how your smartwatch syncs with your phone? The magic behind these connections is a technology called a Personal Area Network (PAN).
This article will explore what a personal area network is, its key components, its purpose, and the different ways it is used in our lives.
In simple terms, a personal area network is about creating a small, wireless network that allows devices close to each other to share data and communicate.
From smartphones and wearable gadgets to smart home devices, PANs form the foundation of our connected world, making it easy for us to control, monitor, and share information.
A personal area network, or PAN, is a type of computer network that connects devices within a small area, usually around a person’s immediate surroundings.
These networks are designed for easy communication and data sharing between personal electronic devices like smartphones, tablets, laptops, and wearables.
The key feature of a personal area network is its limited range, typically up to 10 meters (or 30 feet) from the main device or user. This close-range connectivity ensures secure and efficient data exchange tailored to individual needs.
Read Next: What Network is 0912 in Nigeria? | Network provider
A personal area network consists of several important components that work together to enable smooth connectivity and data sharing among devices. They include:
These technologies help devices within a PAN create secure communication channels for exchanging data and control signals.
PANs can be either wired or wireless. Here’s how it works:
1. Wired PANs: These use physical cables like USB or FireWire to connect devices. They are typically used for high-speed data transfer and are often found in home or office setups.
2. Wireless PANs (WPANs): These use short-range wireless technologies like Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, Infrared (IrDA), or Zigbee to connect devices. They are more common and offer greater flexibility, allowing you to move around with your devices without worrying about cables.
The approximate range of a Personal Area Network (PAN) is typically around 10 meters (33 feet). However, the actual range can vary depending on several factors:
Technology used:
Read Also: What Network is 0902 in Nigeria? | Network Provider
Personal area networks can be organized in different ways, each with its benefits. The two primary topologies for PANs are:
For communication protocols, PANs often use:
These protocols set the standards for how data is sent, how devices find each other, and how the network operates.
Here are some common Personal Area Networks (PANs) examples:
1. Connecting a Bluetooth headset to a smartphone
2. Pairing a wireless keyboard and mouse to a laptop
3. Sharing photos between two smartphones
4. Printing documents from a smartphone to a Wi-Fi printer
5. Making mobile payments with a smartphone
6. Sharing contact information between two smartphones by tapping them together
7. Connecting a USB flash drive to a computer
8. Connecting a digital camera to a computer
9. Connecting an external hard drive to a computer
Read Next: What Network is 0905 in Nigeria? | Network Provider
As with any connected system, personal area networks come with security and privacy issues that need attention, such as:
1. Encryption and authentication: To protect data shared over PANs, encryption methods should be used. Devices must verify each other before connecting to prevent unauthorized access.
2. Device management: Regularly checking paired devices helps maintain security by ensuring no unauthorized connections exist.
3. Security risks: Common risks include eavesdropping on communications or unauthorized access. Using strong passwords, keeping software updated, and employing secure protocols can help reduce these risks.
Personal area networks have become essential in our digital lives by enabling smooth connections, data sharing, and device control.
From smartphones to smart home technologies, PANs have changed how we engage with our environment.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative applications of PANs, making our lives more connected and efficient than ever before.
Personal area networks usually have a range of up to 10 meters (or 30 feet) from the central device or user.
The most common technologies include Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, Near-Field Communication (NFC), and Infrared (IR).
A Bluetooth PAN refers specifically to connections made using Bluetooth technology among compatible devices such as smartphones or headphones.
While generally safer than larger networks due to their limited range, security relies on proper encryption methods and device management practices. Regular updates and strong authentication can significantly enhance security.