Physical Address
60 Ekwema Cres, Layout 460281, Imo
Physical Address
60 Ekwema Cres, Layout 460281, Imo

You are not alone when you have ever attempted to install an application on your Android device, particularly when that app is found as an APK file outside the Google Play Store, and in the process, you get the error message such as “There was an issue with the parsing of the package”.
It is a type of installation error that is also one of the most frequent installation snags in Android users, and may stop progress due to either sideloading an app or custom build work.
Android error parsing is a common occurrence that takes place when you attempt to install or open an application but the system fails to read the package file of the application. Essentially, a parse error implies that Android found a bump in the reading of the installation file (APK) of the app.
In this writing, we will discuss what an android error of parsing is, why it occurs (with some examples of parsing) and we will present you with a step-by-step guide on How to Fix Android Parse Error.
In data processing and programming, parsing refers to the processing and transformation of raw data into a form that can be used. In Android, a parse error denotes inability of the system to properly read and interpret the installation package of the app (APK).
When you download an app, the Android APK is read and the contents are translated into the app that will be running on your phone including the AndroidManifest.xml file that defines the app. When this process does not occur, a parse error occurs.
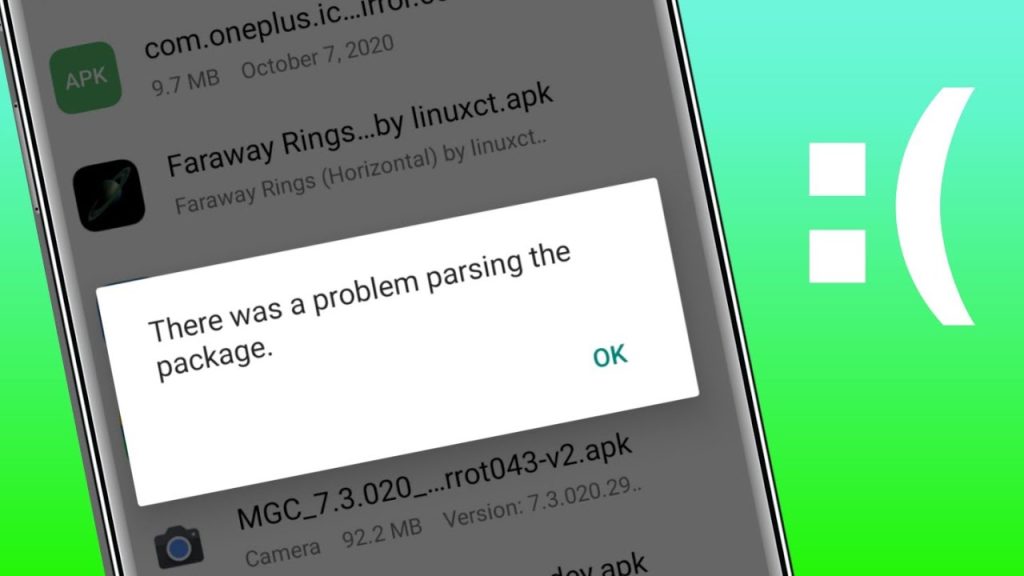
As an example, you could download an APK file to your phone, tap to install it and it gives you a message of There was a problem parsing the package. This means that there is something wrong with the APK or phone environment.
Normally, a parse error will prevent the installation. Your gadget merely refuses to execute the application since it discovered a problem in the package that was not anticipated. This may either be because of corrupted files, incompatibility or the lack of permissions. Once you know what has gone wrong, then you can implement the correct remedy.
Read Also: How to Flash your Android Phone with the Use of a Laptop 2025
Computer Parsing is not uncommon. For instance:
1. Text-to-data Example: Think of a simple application which is downloading a JSON file of weather information which would appear as {“temp:22, condition:Cloudy”}. Parsing refers to the act of transforming that JSON string into something your application can work with – e.g. an object whose temperature field you can access and a condition string. In case the JSON is not structured, the parsing would not be successful and your app would not be able to show the weather.
2. HTML Example: When you enter a webpage, your Web browser interprets the HTML code. It parses the tags (<p>, <div> etc.) and creates the web page based on it. In case the HTML is malformed (through open tags, and so on), the browser might not render the entire page.
3. Android app install example: package installer used by Android, when an APK is installed, the manifest of the app is read. As an illustration, an invalid XML file or an unsupported syntax could be present in the manifest file of an app. Android will not interpret this manifest and it will generate a parse error.
4. Single string parsing: In the simplest form, parsing may refer to the process of turning a string into a number such as parsing a string 123 into 123. In cases where a user input is read by an application or a file, a text is frequently interpreted into data in a structured format. Failure of the parsing will occur unless the text is formatted in the correct way.
In both instances, parsing translates to handling data in order to put it into a comprehensible form. A hit-and-miss error is an error during processing. In the case of Android, the app package is the data.
Repeated Android parse errors can be caused by a number of things. Common reasons include:
1. App/OS compatibility: The application you will install could need a later android version than your phone supports. As an example, an application written on top of Android 12 may not work on Android 9. Read writing requirements always. In the case of too old OS, you may update the software of your phone, or install a version of the app that is supported on your device but is older.
2. Disabled “unknown sources” setting: Android disallows unknown source installations by default. In the event that you attempt to install an APK either through a browser or file manager, go to Settings > Apps and notifications > Special app access and switch the permission to the app (e.g. Chrome or Files) you are using to install.
In older Android versions, you would do it through Settings Security and Occupy Unknown sources. In the absence of this, the system will tend to indicate a parsing error rather than request permission.
3. Corrupted or incomplete APK file: In case the APK file was not downloaded correctly or was destroyed, Android will not be able to decode it. A bad file can be created, e.g. an interrupted download or a broken APK mirror site. It is important to download the apps when the source is reputable. Should you suspect corruption then delete the APK and re-download it over a steady connection.
4. File rename or extension problems: Please ensure that the APK file is correctly named with the extension of the file being “.apk” and that the file has not been renamed. Occasionally, upon moving or compressing the APK, the name or extension can be altered and parsing broken. Renounce it, renounce it and make another attempt.
5. Storage location: In case you are putting it in a microSD card, you can attempt moving the APK to internal storage first. SD card installation may lead to a parse error in other instances because of storage mount problems.
6. Antivirus or security programs: The antivirus or security programs can confuse the installation of APK files and indicate a parsing error. Turn off any security application and re-try. In addition, the Play Store has Google Play Protect (in the Play Store) which may block unknown apps, and you may have to turn it off in the Play Store > Menu > Play Protect > Settings.
7. Lack of enough storage space: In case your phone has very minimal storage, then there is a chance that the installer will fail during unpacking of the APK. Clear up some space (load useless photos or applications) and reinstall.
8. Duplicate package conflicts: When the app has a similar package name and there is an existing app with the same package name installed (this time, probably signed differently), the installer will fail and show a parse error. Uninstall the old version of the app, and install the new one.
9. APK should include special permissions or signature: Certain apps are more secure (such as DRM or signatures required). In case a signature or permission defined in a manifest of an app that your device or other installed apps do not meet, parsing may fail. This is normally rectified with a duly signed APK of the official source.
10. Changes in developer mode: With any alteration to the manifest of the app or recompiling the app, any error in the XML (such as an element missing or syntax error) will result in a parsing error. This will be solved by restoring the original manifest or re-downloading the official APK.
11. Phone bugs: Sometimes, generic parse errors can be a consequence of a bug in the firmware of the phone or a package installer that is out of date. It can be assisted by starting the phone afresh, deleting the information of the package installer, or by updating the phone.
To be more precise, a parse error generally implies that something was identified to be wrong in the APK or the capability of the machine to read it. Based on the above diagnosis (which of the above situations are applicable e.g. outdated OS, corrupted file, security block, etc.), one can apply the relevant fix.
Also Read: How to Flash an Android Phone with the Power Button | Full Guide

Follow these steps one by one to fix a parse error. After each step, try installing the app again.
1. Enable “Install from Unknown Sources”. You are required to allow it in case you are sideloading an app. In Android 8.0 and above under open Settings > Apps and notifications > Special application access > Install unknown apps. Select the application (e.g. your browser or file manager) and allow Allow from this source. On older Android (7.1.1 or older), you can access it by going to the Settings menu and enable Unknown sources. Then retry the installation.
2. Get it either on the official source or on Google Play. The app should be installed in the Google Play Store whenever possible. When the application is available in the Play Store, it should be used to avoid an error of parsing unofficial APKs. In case you need to use an APK (such as it is a beta or it is not in the store), download it on a reliable site (such as APKMirror) via Chrome or file manager to guarantee integrity.
3. Use the correct app version. A program that is developed based on a higher android release will be misread on an obsolete phone. Attempt to install an older version of the application that is compatible with your OS. Previous releases are stored in many developers or APK archives. On the other hand, when you are on a very new Android and you are using a very old application, then check to see whether there is a more modern build of the application and update the APK.
4. Check the APK file. Ensure that the APK has been downloaded and it is not corrupt. Tap the APK in your Downloads folder or in your File Manager to reinstall it. In case the error of parsing remains, remove the APK and re-download it. In some cases, a change in download manager or network rectifies any download problem which is partial.
5. Clear Google Play Store cache (where necessary). In case you received the parse error during an update of an application in the Play Store, go to Settings Apps Google Play Store (and Google Play Services too), and then tap Storage and clear the cache. Then use another attempt to install or update. This is capable of resolving Play Store glitches that appear in the form of parsing errors.
6. Free up storage space. Make sure you possess adequate internal memory. In Settings, go to the Storage and delete some space in case it is nearly full. Uninstalling unused applications or transferring pictures to the cloud will create free space to install the new application, and the error of parsing will be avoided because of the lack of space.
7. Turn off antivirus/ Play Protect. In case there is a security or antivirus application, then temporarily disable it. These applications block unknown APKs at times. Another option is to do it in the Play Store app, where Play Protect should be switched off under the search for apps. Always ensure that you rely on the APK source on the same before doing this.
8. Check USB Debugging (optional). Although unusual, enabling USB Debugging has been reported to bypass some parse errors. To achieve this, open the settings, then go to about phone, and tap on the Build number 7 times in order to see the Developer options. Next go back to Settings System Developer options and enable USB debugging. This step is not normally required by normal user but can be experimented when nothing else fails.
9. Install using ADB (advanced). You can also attempt to install the APK via USB, provided that you have a computer connected via ADB (Android Debug Bridge). Install your phone with the PC, enable USB debugging, and enter a command adb install /path/to/app.apk. It may be successful in cases of direct install failures.
10. Use the Device’s File Manager. Rather than tapping the notification downloaded, open the APK file with the in-built Files or My Files app and tap the APK file. Stock file manager is more efficient in installations in certain situations in comparison to a third party manager.
11. Ensure the package name is exclusive. In case the same application has already been installed, remove it. After that clean up the installer, accessing Settings > Apps, locate Package Installer (or Package Manager) and erase its data. After that, forcefully install the APK again.
12. Restore default privileges. In case you partially installed the app previously, you should access the Settings and Apps and find the app (or its older version) and uninstall it. Then uninstall it and reinstall it afresh allowing you to add permissions where necessary.
13. Factory reset (last resort). When all the above remedies do not give any positive outcome, you should back up your information before carrying out a complete factory reset of your phone. This will rule out the existence of software problems. Once the reset is done, then install the most recent version of Android and then install apps. This is only to be taken as a last resort when it is clear that all the other avenues are exhausted.
Through these steps, you will get rid of the usual sources of Android parse errors. Mostly, the unknown sources setting, the correct APK file, or the space will allow the app to be installed as usual.
Check out: Here is How to Flash your Android Phone without a computer 2025
The APK you are trying to install is not compatible with the hardware or the version of Android you have on your device
When a program is unable to process or interpret a provided formula
allow installation from “unknown sources” or disable “Google Play Protect” and redownload the APK file from a trusted source
Android parse error normally occurs when a third-party (non-Play Store) application is installed or when there is an incompatibility of something to an app or the device used.
Ultimately, the majority of the parse errors can be eliminated after the package is made to be valid in your device and security barriers are tackled. When the error of parsing does not clear even after all attempts have been made, it could be that there is a more significant compatibility problem with the app or device and you can find an alternative application or ask the app developer to help.
Naturally, one should never neglect to be careful when installing APKs not provided by the Play Store. Always use reliable sources, check file integrity where feasible, and ensure your security settings are adequate. These precautions can reduce the chances of encountering a parse error in the first place and will make your devices generally safer.
Android parse error problems can be resolved with patience and a systematic approach to get through the installation with ease.