Physical Address
60 Ekwema Cres, Layout 460281, Imo
Physical Address
60 Ekwema Cres, Layout 460281, Imo

There are many scientific discoveries that have changed the world. The only thing that remains constant is change. At least, it is what the Greek philosopher Heraclitus is reported to have stated. While science and philosophy do not always coincide, Heraclitus’ assertion holds some truth.
Change is inevitable and, in some situations, essential for our species’ evolution. While some changes occur naturally, such as the tides going in and out, others result from scientific discoveries.
Scientific discoveries have significantly shaped human history by advancements that often act as markers defining eras of progress and change. These scientific discoveries, from electricity to gravity, not only influence our understanding of the natural world but also radically transform our everyday lives.
For instance, imagine a world devoid of the electric revolution – utterly unthinkable! Similarly, gravity’s revelation elucidated mysterious planetary motions, proving pivotal in technological advancement that allowed us to conquer space.
This article explores the ensuing narrative traces of the evolution and impact of these two revolutionary scientific discoveries and others shedding light on how they undeniably changed the course of our world and define the way we comprehend the universe. So stay glued and read on!
Scientific discoveries have revolutionized the way we live, influencing almost every aspect of life. From breakthroughs in technology, and medicine, to space exploration, these advances have reshaped our society and outlook towards the world.
Firstly, the discovery of electricity was a game-changer for humanity. Invented by Benjamin Franklin, electricity became the backbone of the modern industrial world. It powers our homes, transportation systems, communication networks, and numerous appliances, which enhances our lifestyle. Today, electricity is indispensable and we cannot envision our lives without it.
The revolutionary concept of gravity by Sir Isaac Newton brought a colossal shift in scientific understanding. Newton’s universal law of gravitation described how objects attract each other with a force proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
This understanding underpinned advancements in physics and astronomy, helping humans venture into space and land on the moon.
Besides, the discovery of antibiotics in the 20th century greatly reduced the risk and incidence of deaths from infectious diseases. The formulation of vaccines, mapping of the human genome and decoding of DNA have all improved medical understanding and interventions.
In essence, scientific discoveries have evolved over centuries and dramatically changed the world. They have unveiled mysteries of the universe, improved quality of life, and fueled economic growth and development.
Yet, the quest for knowledge continues and future scientific discoveries will certainly herald a new era of understanding and existence. Now let’s take a look at these discoveries!
Before then, you can check the 20 technology trends in 2025 that will blow your mind away.
The relentless curiosity and relentless pursuit of understanding have led humans to some groundbreaking scientific discoveries that have transformed our world. Without them, we might still be stuck in the Stone Age, deprived of the comforts and advancements we now take for granted.
From understanding gravity to manipulating electricity, these milestones in human knowledge have paved the way for our modern world. Let’s delve into 12 of these world-altering scientific discoveries.
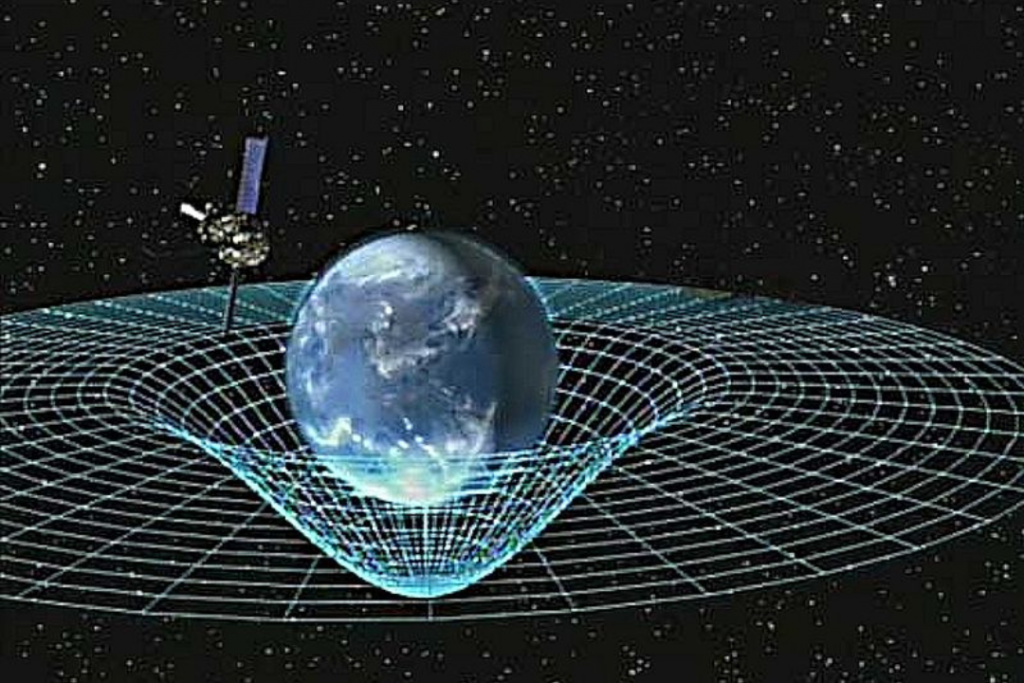
Gravity is the force that pulls two objects towards each other. Anything with mass, from a grain of sand to a gargantuan planet, has a gravitational pull, though the magnitude of the force depends on the object’s mass and proximity to others. It’s this principle that keeps us firmly anchored on the earth’s surface and maintains celestial bodies’ orbits.
Gravity’s existence was first theoretically substantiated by the famous physicist and mathematician, Sir Isaac Newton. His formulation of the law of universal gravitation in the 17th century led to the widespread acknowledgment of gravity as a fundamental force of nature. The gravitational pull concept stemmed from his curiosity after observing an apple fall from a tree.
Gravity’s discovery revolutionized our knowledge of the physical cosmos. Newton’s laws underpin essential calculations used in diverse scientific and technological disciplines, from aerospace engineering to astronomy. Moreover, our comprehension of natural phenomena like ocean tides and seasons is directly influenced by gravity.
This fundamental force helps maintain life on Earth by maintaining our atmosphere and enabling a climate suitable for living. Without a basic understanding of gravity, many human advances in space exploration, skyscraper construction, air travel, and even the utilization of hydroelectric power wouldn’t have been possible.
Today, the understanding of gravity helps us design structures, plan space missions, predict weather patterns, and much more. It is the bedrock of physical reality as we know it.
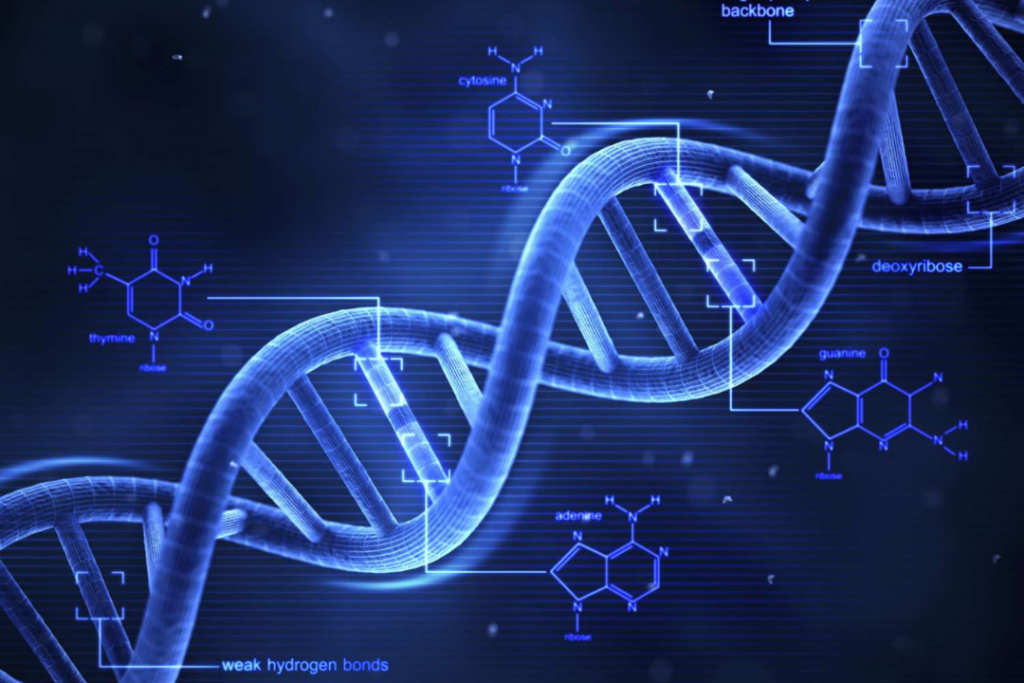

Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a self-replicating substance found in practically all living species and serves as the primary constituent of chromosomes. It is the carrier of genetic information. Its discovery, in the late 19th century, opened a new frontier in the field of biological research.
The discovery of DNA can be attributed to several scientists. Swiss biologist Friedrich Miescher first isolated an unknown substance from cell nuclei in 1869, which he named nuclein. The detailed structure of the DNA molecule, however, was first identified by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953. They proposed the double helix model of DNA, marking a significant breakthrough.
The discovery of DNA completely revolutionized the understanding of human life and heredity. It allowed scientists to manipulate genetic information in organisms, paving the way for gene therapy and genetically modified organisms. DNA testing became crucial in forensics, effectively solving criminal cases.
In addition, DNA sequencing played a key role in tracing human ancestry and understanding human evolution. This significant scientific revelation remains a cornerstone in the fields of biology and medicine, profoundly changing the way we perceive life and the world around us.

The discovery that Earth is not stationary, but in constant motion, is one of the most monumental realizations in human history. It gave a paradigm shift to the age-old belief of a geocentric universe where the Earth was considered the center.
Instead, the heliocentric model that supports the movement of Earth and other planets around the sun came into acceptance. This pivotal shift happened during the era known as the Scientific Revolution.
Nicolaus Copernicus, a Renaissance-era astronomer, and mathematician, is credited for this groundbreaking discovery. In 1543, he published his book De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium (On the Revolutions of the Celestial Spheres), stating that the Sun, not the Earth, is at the center of the universe.
The confirmation of Earth in motion fundamentally transformed how we view ourselves and our position in the cosmos. It was a milestone for astronomy, physics, and all related scientific fields, fostering greater comprehension of our universe’s nature.
The discovery also marked a radical shift in philosophical and religious perspectives, causing disputes that eventually triggered the Scientific Revolution.
Today, it forms the basis for astronomical observations, navigation systems, and satellite technologies, affecting nearly every aspect of our daily lives. Above all, the knowledge of Earth’s motion continues to fuel our curiosity about the expansive universe that lies beyond our planet.
Don’t miss out to read – 7 Hot Tech Jobs in Global Demand 2025
The discovery of insulin in the early 20th century marked a turning point in medical history. It revealed a significant way to control the adverse effects of diabetes, a deadly disease characterized by excessive sugar in the blood and urine. The importance of this scientific finding can never be understated, considering how it presented an immediate treatment for diabetes patients.
The discovery of insulin can be credited to two scientists, Frederick Banting and Charles Best. These Canadians made their momentous breakthrough in the summer of 1921, at the University of Toronto. Their research found that insulin could regulate blood glucose levels, which transformed the world of medical science and healthcare.
The discovery of insulin dramatically altered the health trajectory of diabetic patients worldwide. Before this discovery, diabetes was a fatal disease with no known effective treatment. Insulin’s advent made it possible to manage the disease effectively, thus significantly extending the life expectancy of those afflicted.
Moreover, the understanding of insulin paved the way for advancements in the field of endocrinology, revolutionizing how we treat numerous hormonal disorders. Today, insulin therapy has saved millions of lives worldwide, attesting to its status as one of the most life-changing scientific discoveries.
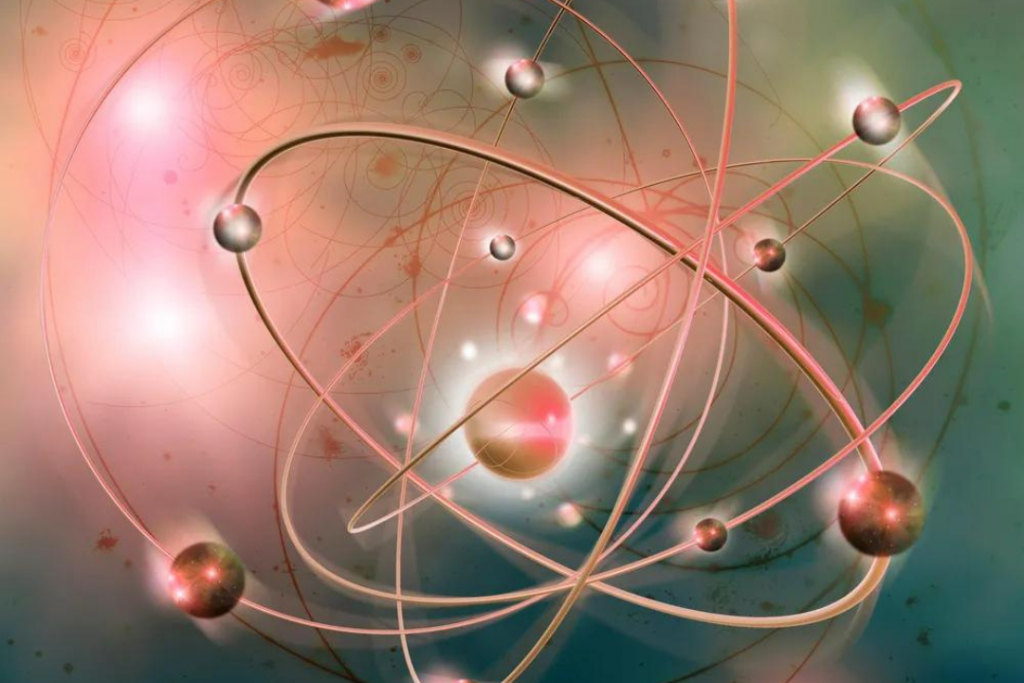
Quantum mechanics, also known as quantum physics, is the scientific study of the tiniest particles in the universe, namely atoms and subatomic particles. It comprises theories and mathematical tools that describe how these particles behave and interact with each other.
One unique and striking feature of quantum mechanics is the principle of superposition, where particles can exist in multiple states simultaneously.
Quantum mechanics was discovered collectively by several great minds during the 20th century. Notably among them were physicists Max Planck and Albert Einstein, who are often credited for sowing the seeds of quantum theory.
Their revolutionary theories were later expanded by Niels Bohr, Erwin Schrödinger, Paul Dirac, and many others, laying the groundwork for modern quantum physics.
Quantum mechanics radically transformed our understanding of the universe. The realization that particles could exist in multiple states at once overthrew centuries-old Newtonian physics and initiated a new era of scientific inquiry.
Furthermore, quantum mechanics has significant practical implications. The invention of transistors and the advent of quantum computing can be directly traced back to the principles of quantum mechanics. From your smartphones to the GPS systems that navigate your cars, quantum physics forms the bedrock of most modern technology.
As we delve deeper into the quantum realm, we stand on the brink of yet another revolution – harnessing quantum phenomena to build quantum computers that would far outperform the capabilities of current digital technology. Thus, the discovery of quantum mechanics was not just an astonishing theoretical breakthrough, but also an indispensable driver of technological progress.
Recently, computer science programs in Africa are doing very well, and you will get to learn about various technological advancements.
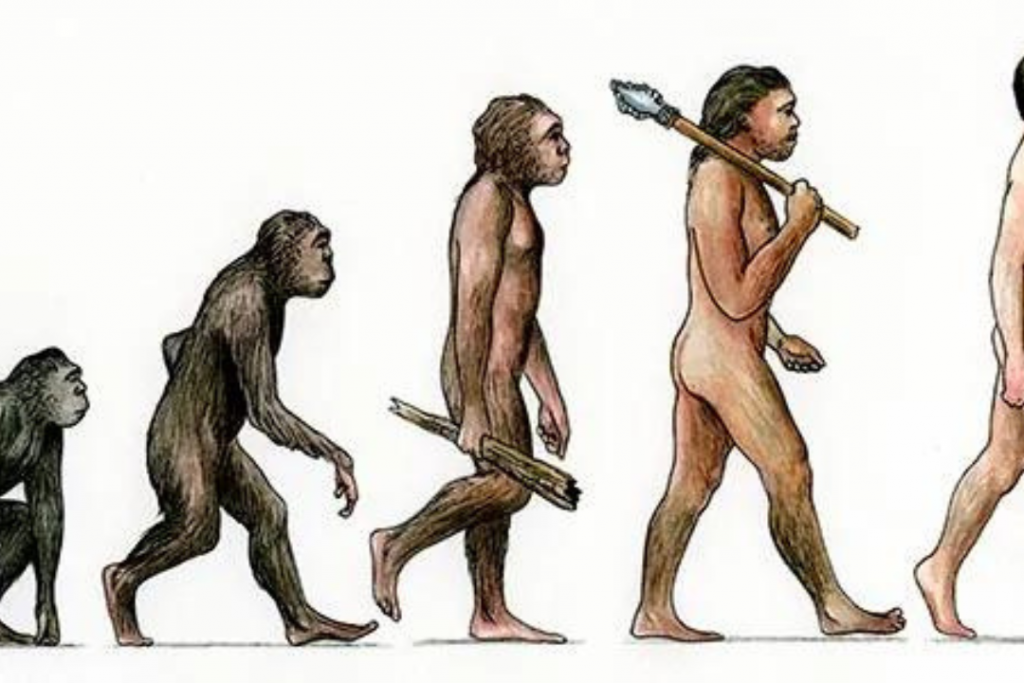
Among the scientific discoveries, the Theory of Evolution is a seminal scientific discovery that underpins our understanding of life on Earth. It is a broad, inclusive concept explaining that species evolve or change over time due to variations in hereditary traits, with beneficial ones becoming more common while harmful traits diminish.
This ground-breaking theory was formulated by English naturalist Charles Darwin during the 19th century. Darwin’s observations of variations among species, particularly during his expedition on the HMS Beagle, led to his pioneering work ‘On the Origin of Species’. Published in 1859, this revolutionary book detailed his extensive findings and observations that built the foundations of evolutionary biology.
Darwin’s Theory of Evolution forever altered the way we understand the natural world. It negated the long-held belief that species were unchangeable, fostering a shift towards a dynamic view of biodiversity.
Today, it guides research in various fields from ecology to medicine. Understanding evolution allows us to combat diseases, protect our environment, and trace our ancestral roots.
Without it, our knowledge about life’s diversity, the relationships between organisms, and the natural progression of species would be significantly limited. Undoubtedly, Darwin’s evolutionary theory is one of the most transformative scientific discoveries ever made.
Check Out the – Nigeria’s Top 10 Tech Brands in 2025

The discovery of electricity marked a significant era in human civilization. It was a scientific breakthrough, revolutionizing the world as we know it today. From the formation of a tiny spark to the introduction of lightning as an electric force, electricity’s existence was demystified, unveiling its potential as a transformative force in human society.
Benjamin Franklin is often credited for the discovery of electricity due to his famous kite experiment. He used a kite and a key during a lightning storm to demonstrate that lightning is electricity. However, it is important to note that understanding and utilizing electricity was the result of collective efforts from several scientists across centuries, including Thomas Edison, Nikola Tesla, and Michael Faraday.
Electricity reshaped every aspect of human life, including industry, technology, and communication. It is at the core of modern society’s operation and advancements, from powering our homes, businesses, and schools to driving medical and technological innovations.
Electricity gave birth to various inventions such as the light bulb, electric motors, telecommunications, computers, and much more. Without it, modern life as we know it would be impossible. It not only changed our physical world but also played a key role in economic development and societal transformation.
In summary, the discovery of electricity has illuminated our world, bringing about a major technological revolution that continually influences how we live, work, and play.
The Germ Theory, also known as the Theory of Contagion, fundamentally changed the field of medicine by asserting that specific diseases are caused by microscopic organisms known as germs. The theory pointed out that many diseases were spread through bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens, revolutionizing the understanding and treatment of diseases.
This groundbreaking discovery was made independently by Louis Pasteur and Robert Koch in the mid-19th century. French microbiologist Pasteur demonstrated that microorganisms cause fermentation and disease, whereas German physician Koch identified specific microbes causing specific diseases, further supporting the Germ Theory.
Germ Theory entirely transformed the field of medicine. With its development, prevention and treatment of diseases have drastically improved, helping to eradicate illnesses and increase life expectancy. It was instrumental in promoting public health measures, which include hygiene practices and vaccinations.
Moreover, the theory steered pharmaceutical advancements leading to the development of antibiotics and other vital medicines. The understanding that microscopic organisms cause diseases not only contributed to medicine but also enhanced human lives, thus impacting the world enormously.

The Big Bang Theory is one of the most significant scientific discoveries explaining the origin of the universe. The theory posits that approximately 13.8 billion years ago, the universe expanded rapidly from a high-density and high-temperature state – an explosion-like event, popularly known as the Big Bang. This revolutionary discovery includes concepts of cosmic microwave background radiation and continuous cosmic expansion.
Belgian physicist Georges Lemaître first proposed the theory in the 1920s. His observations on receding galaxies laid the foundation for this paradigm-changing scientific breakthrough.
However, it was only in the 1960s that the Big Bang Theory was widely accepted, thanks to the pioneering work of scientists Robert H. Dicke, Jim Peebles, David N. Wilkinson, and Peter G. Roll, who detected the background radiation that Lemaître had predicted.
The Big Bang Theory transformed our understanding of the universe’s origins and cosmic history. This profound revelation propelled advancements in various scientific fields like cosmology, physics, and astronomy.
The theory sheds light on mysteries of the universe’s expansion, its age, composition, and evolutionary processes. Besides, it became the foundation for the development of groundbreaking theories, including the theory of relativity and quantum physics.
Most importantly, this discovery redefined human perception of space and time, making us reconsider our place in the vast cosmic panorama. We owe the conception of a dynamic and evolving universe to this ground-breaking scientific discovery, revolutionizing the world of cosmology.
Take out time to read – Tech in Africa: How Nigeria is Leading Africa in Tech Startups
Among the scientific discoveries, Vaccination is a significant scientific discovery that involves the administration of a vaccine to help the immune system develop protection from a disease.
Vaccines contain weakened or inactive components of a certain organism (antigen) that elicit an immunological response in the body. The invention of vaccination started the immunization process and saved countless lives from deadly diseases like smallpox, measles, polio, etc.
The credit for vaccination discovery goes to Edward Jenner, an English physician. He made the first successful attempt in 1796 when he inoculated a 13-year-old boy with cowpox material, and subsequently, the boy developed immunity to the deadly smallpox. Jenner’s work paved the way for the field of immunization.
Vaccination revolutionized public health across the globe. Its advent drastically reduced death and disability caused by infectious diseases. Mass immunization campaigns helped eradicate diseases like smallpox and bring others, like polio and measles, under control.
More recently, the importance of vaccines has been demonstrated by the rapid development and deployment of vaccines against COVID-19. Furthermore, it altered the medical world by emphasizing preventive rather than curative treatment.
Today, vaccination remains a crucial tool in our battle against infectious diseases. It changed the world by enhancing the quality of life, prolonging human lifespan, and protecting future generations from the devastation of microbial threats.
Antibiotics are powerful medications that combat bacterial infections. The initial discovery was groundbreaking, giving mankind an effective weapon against disease-causing bacteria. This medicine works by either inhibiting bacteria growth or eliminating it. The discovery of antibiotics was pivotal in the field of medicine and biology as they fundamentally revolutionized the approach to disease treatment.
The epochal discovery of antibiotics can be credited to Sir Alexander Fleming, a British bacteriologist, in 1928. During a research project, Fleming noticed that a fungus, known as Penicillium notatum, inhibited the growth of Staphylococcus bacteria in a petri dish. This chance discovery led to the development of the world’s first antibiotic, Penicillin.
The advent of antibiotics significantly altered the face of medicine. Fatal diseases like tuberculosis, pneumonia, and other bacterial infections could be effectively treated, vastly reducing death rates and improving the quality of life worldwide.
Before antibiotics, bacterial infections were among the leading causes of death. However, they have since saved countless lives and continue to do so.
The discovery of antibiotics has also paved the way for other medical advances, including successful surgeries, cancer therapies, and organ transplants that depend on managing bacterial infections. The revolution of antibiotics indeed continues to impact public health positively.
CRISPR, short for Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats, is a technology for gene editing that has revolutionized the world of biology and genetics. It is one of the scientific discoveries discovered in 2012, this technology allows scientists to edit an organism’s DNA with great precision and simplicity. It uses an enzyme called Cas9 to cut DNA at a specific point, allowing a specific gene to be removed or added.
The revolutionary CRISPR technology was discovered by two women in science: Emmanuelle Charpentier, a microbiologist now at the Max Planck Institute for Infection Biology in Berlin, and Jennifer Doudna, a biochemist at the University of California, Berkeley. Their groundbreaking research on gene editing led to the discovery and development of the CRISPR-Cas9 system.
The introduction of CRISPR has drastically revolutionized scientific research and opened new realms in genetics. With this, the ability to treat genetic diseases and enhance traits has taken a step closer to reality. From fighting cancer to creating drought-resistant crops, the applications are vast.
The use of CRISPR technology also signifies advancements in personalized medicine, with treatments based on an individual’s genetic makeup. It has not only changed the trajectory of biomedical research but also promised a more promising and healthy future.
Also Read – 20 Technology Trends in 2025 that will Blow Your Mind Away
Scientific discoveries, like electricity and gravity, have undeniably shaped our world, opening pathways for further innovations and improvements. Such breakthroughs allow us to comprehend and navigate the universe in ways our ancestors could never have imagined.
Other discoveries in the realms of medicine, technology, and physics, have equally transformed human existence, extending our lives and expanding our capabilities.
The subject of world-altering scientific discoveries continues to be topical and intriguing. As long as human curiosity and the quest for knowledge persist, we can look forward to more game-changing discoveries in the future.
Scientific discoveries play a critical role in shaping society. They expand our understanding of the natural world, drive technological advancement, improve health and medical treatments, and have an enormous impact on our daily lives.
The impacts of these discoveries on our daily lives are immeasurable. The understanding of electricity has led to the invention of countless technologies like lighting, electric power, electronics, and computers. Similarly, the concept of gravity has led to advancements in space exploration, air travel, and the prediction of natural disasters.
Yes, despite significant advancements, there are many mysteries still left to explore. These include the nature of dark matter and dark energy, the origins of the universe, the possibility of life beyond Earth, the nature of consciousness, and the potential of unifying quantum mechanics and general relativity.